Content
Both accounting for partnership and accounting for corporation contains various similarities but is still have differences. Which of the following could be used as a basis to allocate profits among partners who are active in the management of the partnership? 1) Allocation of salaries.2) The number of years with the partnership.3) The amount of time each partner works.4) The average capital invested. A cooperative is a business or organization owned by and operated for the benefit of those using its services. Profits and earnings generated by the cooperative are distributed among the members, also known as user-owners. Typically, an elected board of directors and officers run the cooperative while regular members have voting power to control the direction of the cooperative.
Table 15.2 summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of different types of partnerships. A partnership is legal business structure consisting of an association of two or more people who contribute money, property, or services to operate as co-owners of a business. When discussing partnerships as a form of business ownership, the term person can what is partnership accounting refer to individuals, corporations, or even other partnerships. However, in this chapter, all the partners are individuals. The Internal Revenue Service looks at corporations as independent taxable entities.. Accountants for corporations must understand where the company’s tax liabilities cut deepest and report these findings to upper management.
Partnership Accounting
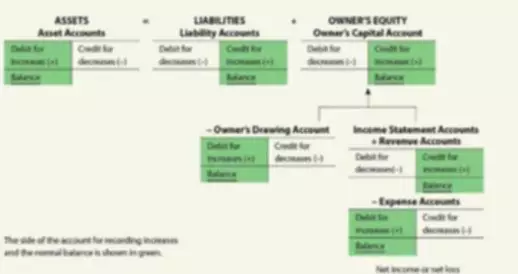
As ownership rights in a partnership are divided among two
or more partners, separate capital and drawing accounts are
maintained for each partner. Dissolution occurs when a partner withdraws (due to illness or any other reason), a partner dies, a new partner is admitted, or the business declares bankruptcy. Whenever there is a change in partners for any reason, the partnership must be dissolved and a new agreement must be reached. This does not preclude the partnership from continuing business operations; it only changes the document underlying the business.
What is the difference between partnership and limited company accounts?
In limited companies, the shareholders own the company, but the directors are responsible for operating it. Whereas in a partnership, the partners both own and run the business. A general partnership is relatively simple to set up. It requires multiple owners to jointly own and run the business.
The corporate tax rate is often lower than the individual tax rate. In a limited partnership, limited partners only act as investors, while general partners share ownership duties. If a retiring partner agrees to withdraw less than the amount in his capital account, the transaction will increase the capital accounts of the remaining partners.
Disadvantages of Organizing as a Partnership
The partners agree to admit Partner C to the partnership
for $7,000. If partners pay themselves high salaries, net income will be low, but it does not matter for tax purposes. Partner compensation and allocated net income are considered ordinary income for tax purposes and as such are reported on the form 1040. It does not matter whether or not a partner withdrew any amount of money from his capital account. But there is also an additional risk in joining a partnership.

A corporation, on the other hand, is owned by shareholders. For-profit corporations reinvest profits in the business and pay out dividends to shareholders. The main difference between a partnership and a corporation is the separation between the owners and the business.
Dissolution of a Partnership
Even more importantly, a corporation has the ability to issue stock and easily transfer pieces of ownership in the company to third parties. This makes corporations the preferred business structure of most investors. In particular, investors like C-corporations because they can purchase preferred stock in your business. As your company grows, stock will increase in value and the investor can earn a nice return on their investment.
Corporations are separate from their owners, but in partnerships, owners share the business’s risks and benefits. Adjustments are made for guaranteed payments, as well as for depreciation and other expenses. As a result, accounting income of a partnership is adjusted, or reconciled, to taxable income.
Fully explain how is accounting for a partnership is different from accounting for a corporation. B. The right of co-ownership in the business property can be transferred to a new partner without the consent of other existing partners. Nonprofits are often called 501(c)(3) corporations — a reference to the section of the Internal Revenue Code that is most commonly used to grant tax-exempt status.
- Business partners simply file Schedule K-1 along with their personal 1040 tax return.
- The land could be reported as an asset by the business-type activities in the governmental wide financial statements.
- A partnership can be a general partnership, a limited liability partnership, or a limited partnership.
- Partners often share in deciding how to hire and monitor managers.
- For example, if there is a profit in the income summary account, then the allocation is a debit to the income summary account and a credit to each capital account.
- It can also be hard to raise money because you can’t sell stock, and banks are hesitant to lend to sole proprietorships.
Compensation for services and capital are guaranteed payments. The partnership agreement may specify that partners should be compensated for services they provide to the partnership and for capital invested by partners. Table 15.1 summarizes some of the main advantages and disadvantages of the partnership form of business organization.
Share Question
The specifics of profit sharing will almost certainly be laid out in writing in a partnership agreement. In particular, in a partnership business, all partners share liabilities and profits equally, while in others, partners may have limited liability. There also is the so-called « silent partner, » in which one party is not involved in the day-to-day operations of the business. Individuals or groups who own shares of a company’s stock are known as stockholders.
Corporations have a more formal management structure than partnerships. They hold regular meetings that determine company policies and management. Shareholders usually don’t have a lot of day-to-day involvement in the company’s management; instead, they oversee managers who handle daily business activities. Profits and losses pass through to the individual partners. The partnership reports profits and losses to the IRS and partners include their share of this in the return. Assume now that Partner A and Partner B have balances $10,000 each on their capital accounts.